Polypropylene 3D printing might sound like a mouthful, but it’s the secret sauce that’s about to revolutionize the way we create. Imagine a material that’s as tough as your morning coffee and as flexible as your schedule on a Friday night. That’s polypropylene! This versatile polymer is making waves in the 3D printing world, offering durability and lightweight properties that traditional materials can only dream of.
Table of Contents
TogglePolypropylene 3D Printing
Polypropylene 3D printing utilizes a versatile thermoplastic known for its excellent balance between flexibility and strength. Properties like chemical resistance and low-density make polypropylene a preferred choice for various applications, from automotive parts to consumer goods.
This material offers lightweight solutions, significantly enhancing the efficiency of end products. Durability stands out, with polypropylene exhibiting resistance to impact and wear. In terms of environmental impact, polypropylene is recyclable, adding sustainability benefits to its usage.
Absorbing moisture is minimal in polypropylene, ensuring that printed parts maintain their integrity in various conditions. Users often find that polypropylene prints require specific settings on 3D printers to achieve optimal results, particularly in terms of temperature and bed adhesion.
In terms of applications, industries such as healthcare and packaging frequently adopt polypropylene for its hygienic properties and ability to withstand sterilization processes. Prototyping becomes more efficient due to the material’s quick print speeds and minimal post-processing requirements.
Specific benefits highlight the advantages of polypropylene 3D printing. For example, it lends itself well to producing flexible joints, which are crucial for mechanical assemblies. Users appreciate that this versatility allows for the creation of complex designs without sacrificing functionality.
Benefits of Polypropylene in 3D Printing
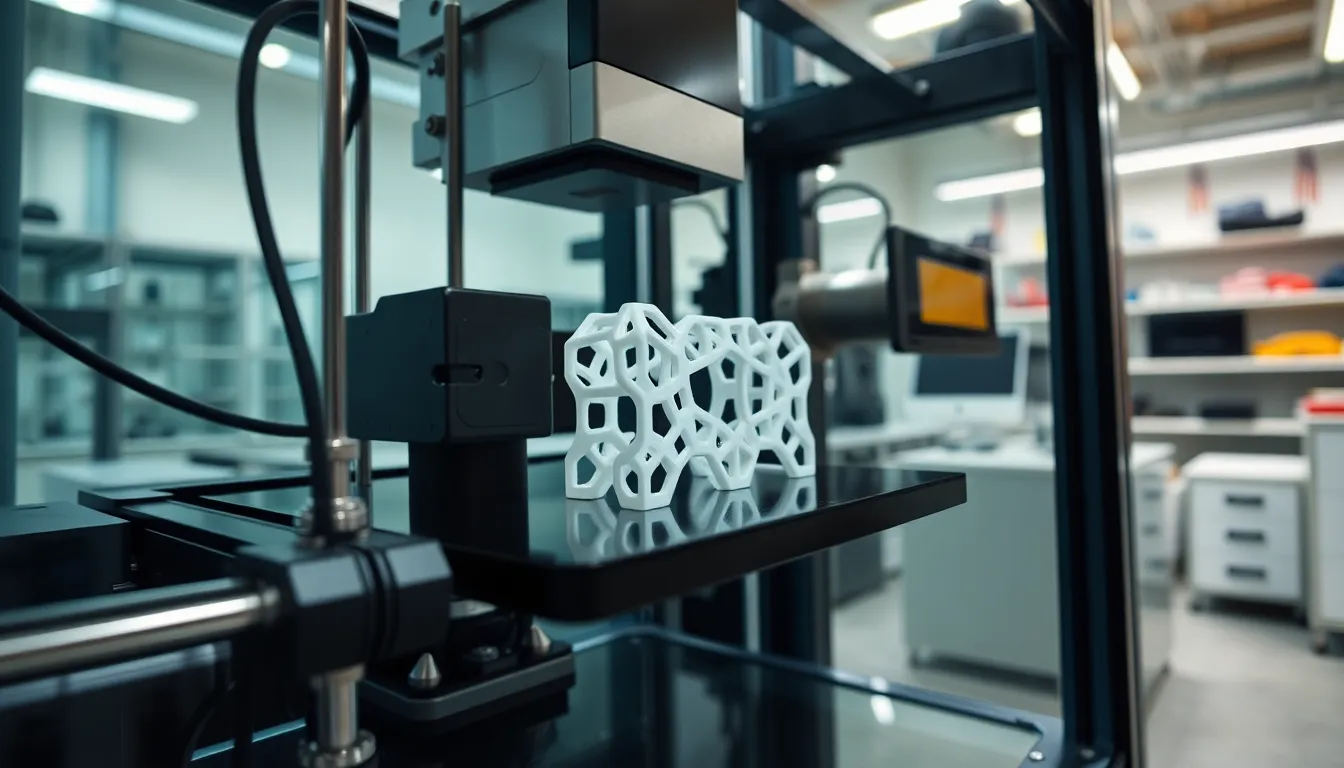
Polypropylene offers multiple advantages in 3D printing, enhancing functionality and versatility across various applications. Its unique properties make it a favorable choice for many manufacturers.
Strength and Durability
Strength and durability characterize polypropylene, making it an ideal candidate for demanding applications. This material withstands impact, wear, and stress, allowing for longer-lasting products. Printed polypropylene parts resist deformation, enabling them to maintain their shape under various conditions. Industries such as automotive and consumer goods benefit from this reliable performance, as it reduces the frequency of part replacements. Moreover, polypropylene’s inherent resistance to chemicals further contributes to its durability, ensuring that printed items can endure harsh environments without deterioration.
Lightweight Properties
Weight remains a critical factor in design, and polypropylene’s lightweight properties significantly enhance product efficiency. The low density of this thermoplastic allows for the creation of robust structures without adding unnecessary weight. It fosters better fuel efficiency in automotive applications and simplifies handling in consumer products. This lightweight advantage leads to quicker production times and facilitates easier transportation. Additionally, when forming complex designs or assemblies, the lightweight nature of polypropylene ensures that mechanical functions remain effective without sacrificing structural integrity.
Challenges in Polypropylene 3D Printing
Polypropylene 3D printing presents several challenges despite its advantages. Issues like adhesion and warping can impact the overall print quality.
Adhesion Issues
Adhesion issues often surface during the 3D printing process with polypropylene. Printed layers frequently struggle to stick to the build plate. It’s essential to use specialized surfaces, such as heated beds, to improve adhesion. Some printers require adjustments in temperature settings to enhance layer bonding. A poorly adhered base layer can lead to failures or inaccuracies in the final product. Selecting the right adhesive can also make a significant difference, helping prevent the parts from lifting or curling during printing.
Warping and Shrinkage
Warping and shrinkage frequently occur when using polypropylene in 3D printing. Significant temperature variations cause the material to contract as it cools. This contraction can lead to distortion of parts during the printing process. Maintaining consistent temperatures in the environment and the printer is crucial for minimizing these issues. Effective print settings also help mitigate warping risks, allowing for better dimensional stability. Choosing low-shrink formulas or blends can further reduce the likelihood of warping, ensuring more reliable print outcomes.
Applications of Polypropylene 3D Printing
Polypropylene 3D printing serves various industries due to its unique properties. Its versatility allows for efficient production in multiple applications.
Packaging Solutions
Polypropylene excels in creating packaging solutions that require durability and flexibility. It supports the production of lightweight containers, reducing shipping costs while maintaining strength. Print designs accommodate airtight seals, enhancing product preservation. Customizable features enable brands to offer unique packaging that stands out on shelves. High chemical resistance allows polypropylene to store a range of materials, from food to pharmaceuticals. Recyclability of printed polypropylene adds a sustainability aspect, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Automotive Parts
In the automotive industry, polypropylene is sought for producing various components. Its lightweight nature contributes to improved fuel efficiency, making it ideal for parts like trims and interior elements. The material’s strength ensures resistance to impact, enhancing safety in automotive designs. It enables manufacturers to create complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve. Moreover, polypropylene’s resistance to wear and chemicals plays a crucial role in extending the life of automotive parts. Fast print speeds facilitate quicker prototyping, allowing manufacturers to refine designs rapidly for better performance.
Conclusion
Polypropylene 3D printing stands out as a game-changer in manufacturing. Its unique combination of strength flexibility and lightweight properties makes it an ideal choice for a variety of applications. Industries benefit from its durability and resistance to wear while enjoying the advantages of quick production times and reduced material costs.
Despite challenges like adhesion issues and warping the rewards of using polypropylene far outweigh the difficulties. With the right printer settings and techniques manufacturers can harness this versatile thermoplastic to create innovative designs that meet modern demands. As the technology continues to evolve polypropylene’s role in 3D printing will likely expand further solidifying its place in the future of manufacturing.
